It’s hard to think about a time without logistics automation.
Right from procurement to fulfilment and delivery, automation is deeply embedded in every logistics process in the supply chain.
But the advancements don’t stop here. According to studies, the global warehouse automation market is expected to exceed $30 billion.
It means the industry is embracing automation at a striking rate with the objective of simplifying processes and setting themselves up for long-term success.
To understand the role of automation in logistics in detail, we’ve put together a guide that explicitly explains why automation in logistics is important and how the industry can navigate and adapt to new technologies.
Let’s check it out.
What is Logistics Automation?
Automation in logistics is the use of digital technologies in processes to make your business’ logistics function more efficiently. It is the process of equipping your operations with control systems, software, and automated machinery that ultimately leads to improved time and quality.
For example, the use of advanced types of machinery like automatic guided vehicles, robotic arms, vertical lift modules and other automated storage and retrieval systems for the movement of goods or CRM and ERP systems to automate inventory management and demand forecasting, etc.
Businesses that successfully integrate their logistics management systems into their supply chain ecosystem can truly transform and automate processes to improve the bottom line.
Why is Automation in Logistics Important?

Logistics is one of the most time-consuming and expensive processes in the entire supply chain. As a result, companies are scrambling to find methods in order to reduce overall costs while meeting the changing expectations of customers at the same time. Logistics automation is the need of the hour for numerous reasons.
1. Reduction of Errors
No matter how capable or smart your employees are, you should know that at the end of the day, a weary human mind is prone to making errors and understandably so. It can range from something as minimal as a typo or mistaking a number for something else. However minor the error may be, it eventually turns into a snowball effect that hugely influences the bottom line.
The problem doesn’t just end with the error, it also entails the associated costs with it. Think of all the resources that are wasted on tracking the mistakes and rectifying them. It hampers productivity and cuts revenue. The idea is simple — machines don’t feel tired or need a holiday. It can do its job without any intervention, for longer hours, and with the consistency needed in a supply chain.
2. Cost Savings
Since automation in logistics fills in gaps in processes and key decisions, it significantly reduces operational costs. Right from choosing the most cost-effective carrier to choosing an optimized route, or stocking the right amount of inventory to optimizing the load of each shipment, automation plays a critical role in cost savings across all these processes.
Automated stock inventory also aids warehouses in reducing expenses related to storage and managing unexpected demand peaks by ensuring stocks fulfil orders. It takes over the repetitive workloads such as data entry so that your teams can focus on higher-value tasks and serve customers in less time.
3. Real-time Data
The modern supply chain is backed by concrete data. And that is only possible through logistics automation. For example, software systems like inventory management provide access to real-time data on how much inventory warehouses should stock, how much they should dispatch, and how much they should reorder.
Logistics software also provides real-time freight rates that help freight providers to plan for freight capacity and offer competitive rates while reducing the cost of manually extracting data. And this data is based on trends and history. It provides you with the power to view the total cost of decisions and reduce the risks associated with bad decisions.
4. Scalable Opportunities
Automation has allowed businesses and online stores to commit to hundreds of millions of customers for timely deliveries every day. For small businesses, automation ensures steady and secure growth. And for large companies, automation can help you ensure that your supply chain is capable enough to handle large volumes of orders and doesn’t fall apart when you expand your operations and take on more clients. Automation also makes it easier to replicate your operational success in one warehouse to multiple locations.
5. Better Customer Service
It is impossible to speak of deliveries and not mention customer service. Studies show that more than 26% of customers expect speedy delivery (same/next day deliveries) and more than 27% pay heed to the cost and convenience of deliveries before making a purchase. Failure to meet these expectations prompts the customers to find potential competitors that can fulfil their requirements.
Automation in logistics such as transportation management systems facilitates real-time tracking and auto-pick which facilitates companies to provide seamless deliveries at low costs. It also improves visibility so that consumers are also on the same page when it comes to cost and delivery.
6. Increased Visibility
Automation makes it possible for collaboration between departments in the supply chain. Every department can see where the inventory is and how it’s moving. It allows managers to have greater control over the processes through quick and easy communication.
The data also makes it easier to manage stock levels and price points. In certain cases like food, it makes all the more sense to have visibility so you deliver the goods at the right time.
7. Faster Shipping Times
The growth of eCommerce is unprecedented in recent times, making the online shopping space a competitive one. One of the best ways to stand out from the competition is to meet the impossible delivery expectations of consumers.
Automation in logistics accelerates the speed at which products move along the supply chain to the end-user and allows companies to commit shorter delivery times to consumers. Delivery systems optimize routes that allow you to manage speedy deliveries as well as plan return logistics across multiple locations.
Areas of Logistics Automation
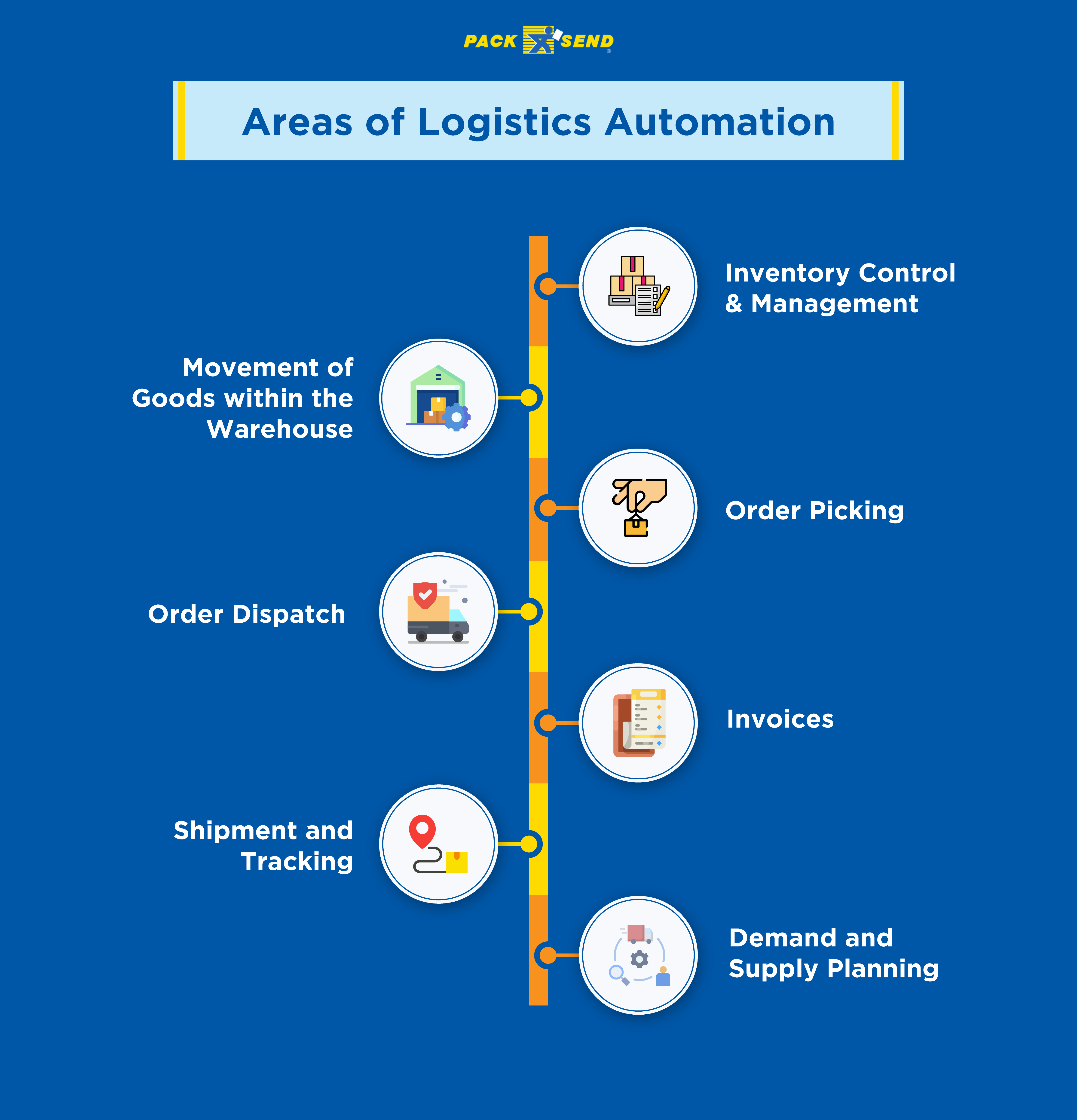
The logistics processes comprise many activities and automation can be integrated into each of them in some or the other way.
1. Inventory Control & Management
Inventory controls the major part of logistics management. The right quality, quantity and storage facility determines the efficiency of other processes in the supply chain. Logistics automation in inventory envelopes tracking the location and number of inventory across each warehouse.
The inventory control systems provide information on how much inventory is stored at a given time and what items are needed to replenish them so that you don’t have to manually track stock levels.
You can easily check if there are any shortages or overstock and thereby reduce the costs associated with storing excess inventory. You can also react swiftly to potential issues within the supply chain.
2. Movement of Goods within the Warehouse
Logistics is an industry that still relies heavily on the manual labour of lifting and moving the goods around the warehouse and loading and unloading goods. One of the most common solutions in logistics automation is the installation of automated storage systems capable of transporting large quantities of stock and movement of goods within the warehouse.
For example, using pallet conveyor systems streamline goods flows from production and pallet shuttle for the purpose of product loading and unloading times. Warehouses are also using stacker cranes which boost productivity when removing and depositing goods on the shelf. These logistics automation systems move up and down the aisle along guide rails.
3. Order Picking
Order picking is one of the most essential but also one of the costliest functions in logistics. It is the process that is most prone to errors and is also time-consuming. To address the complexity associated with the process, many companies are leveraging Warehouse Management Systems to coordinate the entire process of automated order processing. It includes slotting the various SKUs, finding the nearest locations of the orders, and allocating the orders to specific warehouse locations.
WMS is also equipped with semi-automated picking techniques such as voice picking, and pick-to-light in which the software guides the managers and operators in picking orders from shelves and showing what quantity of stock to pick for each other.
Integration of such technologies with warehouse management systems makes it easier for companies that have to deal with high-demand volumes. It reduces the time and risk of errors in order processing.
4. Order Dispatch
Order dispatch is the process of order fulfilment that refers to the process of scheduling and managing the movement of shipments and goods to meet customer demands. It ensures the timely delivery of goods which meets the quick delivery requirements of the customers.
Logistics automation is replacing traditional loading docs with automatic truck loading like forklifts and systems that are designed for firms with a large volume of orders. They include conveyors and lifting platforms that speed up the loading of goods into the vehicles and movement within the warehouses.
It also helps with optimising labour utilization and improving safety within the facility by reducing the risks of accidents which normally occur due to collisions.
5. Invoices
Every logistics company deals with tons of paperwork and important documents on a daily basis. These documents include contract agreements, bills of lading, transport and vehicle documents, freight bills and so on. Not only is it a hassle to handle physical copies but it also slows down the process with a lack of real-time tracking.
To address these challenges, logistics companies now use the Invoice data capture. It is the process of managing a supplier invoice from the invoice receipt to intercept and validate invoices by a system. Automated invoice data capture includes a set of tools that automates the task of invoice capture through artificial intelligence and machine learning.
6. Shipment Tracking
Automation in logistics has enabled companies to have a good shipment tracking system that simplifies supply chain management. How?
For starters, it allows suppliers, customers and logistics companies to track shipment data on a single dashboard. It ensures a seamless flow of data and real-time, automated shipping updates on the movement of all domestic and international freight.
It also makes it possible for companies to make data-driven decisions and prepare for uncertainties with the help of increased visibility. When you’re constantly updated about the movement of goods and their current locations, you can get a heads-up before every potential disruption and are better equipped to deal with delays.
Efficient shipping and tracking automation also brings the customers in the loop and shows them where their products are at all times and when they can expect the delivery. It gives you greater control over final delivery dates and responds to unexpected queries.
7. Demand and Supply Planning
The logistics industry is reaping the benefits of Robotics Process Automation where AI is trained to mimic human intelligence to automate business processes. This very combination of RPA and AI is perfect for accurate demand and supply planning. AI predicts sales and generates forecasts based on real-time data which takes into account the future sales target, seasonal demand data, historical data, current inventory levels, price trends, etc.
The use of AI is by far one of the most promising technological applications in the supply chain. The inclusion of internal and external influencing factors, social reviews, and the performance of similar products online, gives a realistic depiction of the demand and supply scenario. If this is automated, supply chain managers can take on more strategic tasks.
AI-enabled demand forecasting enhances logistics for supply chain networks that can traverse through manually controlled networks. With accurate data, you are also better equipped to respond to customer needs in a short time and reduce sales losses due to out-of-stocks and improve the overall customer service level of manufacturers.
Types of Logistics Automation Systems

To become technologically competent in logistics, you need to embrace the logistics automation systems toolkit that ensures the success of your digital endeavour. Let’s check out the systems that are included in the same.
Inventory Control Systems
An inventory management or control system is a logistics automation solution that manages and tracks your goods through the supply chain. It integrates with other systems and manages shipping, purchasing, receiving, and so on under a single dashboard.
An efficient inventory control system will automate all the necessary processes in inventory and provide a comprehensive view of what inventory you have, where it is, and when you need to reorder to keep your stock according to the required demand.
Inventory control systems are divided into the perpetual inventory system and the periodic inventory system. While perpetual inventory management systems track inventory in real-time, periodic inventory systems update inventory by a physical count of goods on hand at specific intervals. Realistically, periodic inventory systems are only feasible for small businesses that don’t deal with a high volume of inventory at once.
2. Predictive Analysis
Currently, 31% of logistics companies already use predictive analysis. This percentage is expected to grow to 48% in 2025. It shows that predictive analysis is a growing trend because logistics companies prefer being a step ahead in terms of supply chain operations.
In the warehousing framework, predictive analytics consists of implementing statistical techniques to the data generated in a logistics facility. The purpose of predictive analysis is to conclude a detailed analysis of operations, plan resources, and measure business performance.
The data conclusion is derived from mathematical models that determine the degree of probability based on patterns and trends. Companies can know the correct product quantities to store for each SKU and decide the number of operators and shifts required to prevent interruptions in the supply chain.
3. Warehouse Robotics
Robotics has been one of the most disruptive technologies in warehousing. Warehouse robotics include automated forklifts, collaborative mobile robots, automated storage systems, and drones. They are used to perform activities storing and retrieving at a consistent pace and accuracy.
Investing in warehouse robotics is expensive so it needs to be done with adequate planning and assessment of existing assets. But with it, you can promote a safe working environment for your workers and promote efficiency in the movement of goods in loading, unloading, and within the facility.
4. Data Capture Software
To automate the paperwork, logistics companies use a technology called data capture software. It processes data from documents and eliminates the need for manual data entry. The system uses a combination of Optical Character Recognition (OCR), advanced pattern recognition, and anchor keywords through which it extracts data from various documents.
This technology is able to extract numbers and characters from digital invoice formats. Data capture software reduces the errors from manual data entry and saves considerable time processing day-to-day documents.
5. Asset Monitoring and Tracking Software
We often associate logistics with a highly risky affair. And most of that risk comes from transportation as it is where the goods are most vulnerable to damage, theft, and spoilage. A mishap in transportation means a tarnish of reputation, and loss of customers and revenue.
Asset monitoring and tracking systems in logistics helps you track the status of your inventory as they move across the chain. It evaluates the shipment location, temperature, pressure, and humidity, to ensure the goods are transported to the right places in the right conditions. Real-time monitoring facilitates companies to be quick on their toes and intervene as soon as they detect an anomaly.
6. Robotic Process Automation
In the most basic sense, robotics process automation uses automation technologies to mimic administrative and mundane human tasks such as extracting data, filling forms, etc. It controls every function of robotics in operation and necessitates implementing digital transformation within the organization.
The purpose of robotic automation is to minimize staff administration costs and reduce human errors. Robotics process automation clubs all the logistics automation activities under a single system and brings new opportunities in invoicing, 3PL logistics provider rate comparisons, batch processing, etc.
Tips for Implementing Successful Logistics Automation

While it’s clear that automation in logistics provides all kinds of benefits, we still don’t know how you can implement automation at different levels. Listed below are some points you can consider for successful logistics automation implementation.
1. Examine the Current Process
Before bettering your processes, you need to know which areas require automation and which gaps need to be filled. Automation may not always be the best idea for certain tasks and you don’t want to invest efforts in the wrong places. Get a good overview of your logistics and based on the data, you can know the level of inefficiencies that needs to be addressed with automation.
While some automation systems are a must-have such as inventory control systems, not every warehouse needs to have robotic arms or forklifts. These decisions will depend on your scale of operations and the number of inventories you usually stock on average.
2. Establish Clear Communication Beforehand
Implementing logistics automation isn’t a one-time project. You adopt new technologies as you grow and it requires constant assessment of budgets, workforce, and technical expertise. Have a dedicated project manager that can provide full-time commitment and ensure that all your departments are equally involved in the project.
Provide training to departments that may need it and outsource certain roles if you don’t have the internal expertise for it to prevent knowledge gaps in the future. Consider the constant need for upgrades and maintenance and choose the right set of maintenance schemes.
3. Work with Future Scenarios
When you take the decision of incorporating logistics automation into your supply chain, you need to consider your future projections and an emphasis on growth over time. With automation, you’re in for the long haul. You need to examine the capability of the warehouse, including automated technology to define future requirements. It will ensure that you build a warehouse matching the exact needs.
For example, you currently only have a single warehouse due to fewer orders. However, as your orders increase, you’ll need to resort to contract warehousing and partner with 3PL providers and scale your delivery process. Only then, it makes sense to integrate a shipping technology that integrates multiple warehouses. In simple terms, your logistics automation should be reflective of your growth stages.
4. Estimate Risk Management
Involving automation in logistics will pose new risks. It is ideal to work through these risks, analyse them, and prepare adequate measures to minimise their impact. Consider the risks of the operation that may come into play like downtime, repairs, etc. And not just the technology but calculate the risks associated with packaging, design, and quality so that your systems can function properly.
A robot may not always stop due to technical failure but due to a poorly packed product or disorganized inventory. Keep a bandwidth to endure the failures of pieces of machinery and systems and adverse developments. Testing operations should be a critical part of the automation process.
5. Adopt a Comprehensive Solution
By now you’d know that automation is multi-faceted in logistics. You cannot simply implement an inventory control system and call it a day. If you’re an online store that is operational in multiple locations and requires intricate logistics planning, you need to embrace yourself for a comprehensive logistics automation solution.
When we say comprehensive solution, it means involving multiple software as well as departments. Once you have multiple systems, you can simply integrate them with each to get consolidated data under a single view.
Finishing Thoughts
In all of the eCommerce functions, we can agree that logistics is the most challenging one to fulfil. It is heavy on the pocket, risky, and heavily dependent on multiple factors that sometimes aren’t in our control. In such a scenario, automation in logistics is a blessing for many modern logistics companies that are navigating their operations in a competitive space.
However, with so many factors to consider, it is ideal to partner with a logistics company that can provide various logistics solutions for you. You can contact us at PACK & SEND to get a comprehensive range of logistics solutions for your business which can be customised to support your operations. With years of experience, you can rely on us to handle all aspects of your customer order process, right from picking and packing, to shipment, and deliveries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is logistics automation?
Automation in logistics is the use of digital technologies in processes to make your business’ logistics function more efficiently. It is the process of equipping your operations with control systems, software, and automated machinery that ultimately leads to improved time and quality.
What are the benefits of logistics automation?
Businesses are leveraging logistics automation to reduce the errors stemming from human labour, save costs, access real-time data, and have a sustainable plan for growth. It also increases visibility in the supply chain and leads to faster customer deliveries.
What technologies are used in logistics automation?
The logistics automation ecosystem is inclusive of inventory system control, warehouse robotics, shipment and tracking software, data capture software, predictive analysis, and robotic process automation systems.
