Here's a quick riddle for you: What's a challenge that both retailers and customers face but see differently? If you guessed "retail returns," you're right on the mark!
For customers, retail returns are like a safety net. Returns ensure they're satisfied with their purchases. They are customers’ way of making sure they always get what they want.
But for retailers, eCommerce retail returns can be a bit more complicated. It involves handling the reverse logistics and item restocking and managing its financial impact. Mishandled, they can eat into profits and create operational headaches.
In this blog, we'll dive into retail returns and why they matter for retailers. We'll discuss ways to improve product returns management and turn them into assets.
What is a Retail Return?
A retail return is a process initiated by a customer wishing to return a purchased product. This could be due to various reasons. Such as not liking the product, receiving a damaged item, or changing their mind. The retailer's role is to handle product returns, offering a refund or a replacement.

Let's say you operate an online clothing store. A customer who recently bought a dress. A customer contacts your customer support to start a return because of the size issues. As the retailer, your job is to guide the customer on how to return the dress. This might include giving them retail return instructions and a return label. Once you receive the dress in good condition, you can either refund or offer a replacement.
How Does the "Product Returns" Process Work?
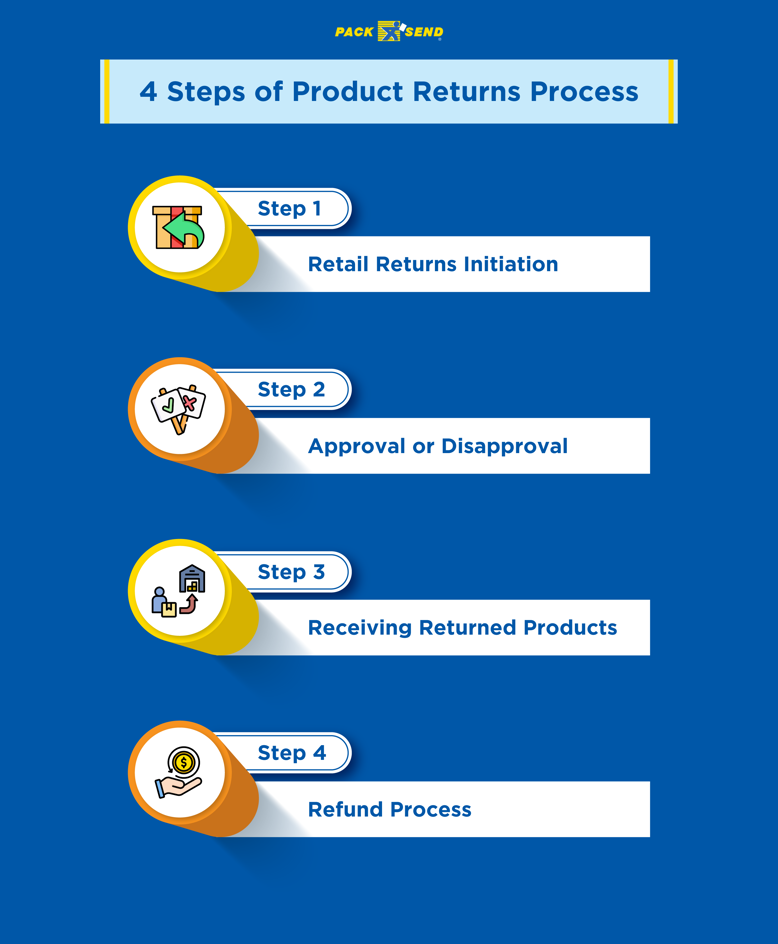
The returns process, also known as reverse logistics, unfolds in several steps:
Step 1: Retail Returns Initiation
The process begins when a customer decides to return a product, from an online or offline store. The customer specifies reasons for returns. They also state whether they want an exchange or refund.
Step 2: Approval or Disapproval
On assessing the request, the company decides whether to proceed with the return. Some companies engage third-party logistics (3PL) providers to streamline return and retail fulfilment.
Step 3: Receiving Returned Products
The 3PL collects the product return from the customer and delivers it to a designated location. The retailer then conducts a physical inspection of the returned product as per its return policy. They must choose whether to recycle the item for useful parts, repair or refurbish it, resell it, or dispose of it.
Step 4: Refund Process
Based on the product's condition and return policy, retailers figure out its response. It might involve offering a refund, exchange, store credit, or product repair.
What Is Retail Returns Management and Why Is It Important?
Returns management is the systematic process by which retailers and eCommerce stores handle and control product returns initiated by customers. It combines elements of customer support, logistics, and inventory management.
Returns Management focuses on the efficient handling of returns in retail. This is crucial for businesses because it directly impacts customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and overall profitability of the business.
Efficiently handling product returns can lead to substantial cost savings by repurposing undamaged items and restocking them for future resale.
Product returns in eCommerce often present greater complexity compared to brick-and-mortar stores. That’s because eCommerce returns often involve returning the product back to the seller, adding more costs and logistical challenges to the mix.
Here are the key steps in a return management process:
1. Return Request: Customer requests a return due to defective or incorrect items or dissatisfaction.
2. Review for Authorization: Retailer checks return requests against their return policy (timeframe, eligibility).
3. Generate Return Label: Approved returns receive a shipping label for customer use.
4. Secure Packaging: The customer ensures the item is packaged with all accessories, tags, and packaging.
5. Ship the Return: The customer sends the item using the provided label or designated method.
6. Receive and Inspect: Retailer receives, inspects for damage, and checks completeness.
7. Disposition Decision: The retailer decides on restocking, refurbishing, recycling, or disposal.
8. Resolution: The retailer discusses resolution options with the customer (refund, exchange, credit, or repair).
9. Process Refund/Exchange: The retailer implements the chosen resolution.
10. Update Inventory: Retailer adjusts inventory based on disposition decision.
11. Data Analysis: Analyze return data for trends, product return issues, and process improvements.
12. Reverse Logistics: Reverse logistics for returns to the manufacturer or supplier. May involve transportation coordination and inventory management.

Why Is Retail Returns Management Important?
Retail returns, especially in online shopping, have evolved into a well-established practice. When we buy stuff online, we can't try it out first. So, having the option to return items for free is something most stores offer.
So much so that the concept of free returns is being carried over across all retail channels thanks to omnichannel retail. In the past, you could only return things if the store didn't meet your expectations. But now, it's much easier to return things for any reason, even if you just changed your mind.
However, the traditional retail supply chain is linear, typically ending when the product reaches the consumer. Any product reentering the supply chain after the sale is seen as an 'exception.' Handling these exceptions is both expensive and complicated. It increases the cost of service and reduces profit margins.
In recent years, rising product returns have worried retailers and their profits.
According to a study by SML, in 2022, retailers found that about 30% of their sales resulted in returns. This is significantly higher than the 10% returns level of in-store purchases.
Furthermore, on average, about 42% of these returns were resold at a lower price, and 12% were not resold. Retailers mentioned that the average discount applied to these items was around 38%.
High return rates are clearly taking a significant bite out of retailer profits. In the current economic climate, businesses can't ignore this challenge any longer. Retailers should view retail returns as an integral part of the customer journey. Handling returns right can boost customer loyalty and advocacy.
To address this issue effectively, retailers need a streamlined and cost-effective return management process that ensures returned items can be quickly reintroduced for sale.
Here are some more reasons to have efficient retail returns management:
1. Cost Savings
Effective returns management can help with significant cost savings. Restocking fees or store credit instead of refunds can help control expenses. Moreover, streamlining the return process reduces costs linked to shipping and handling.
2. Inventory Optimization
Returns management contributes to better inventory control. It ensures efficient flow of returned products through the supply chain. It also addresses the financial impacts of lost sales and restocking. Tracking product returns helps adjust stocking strategies, reducing excess inventory and enhancing efficiency.
3. Customer Delight
Smooth returns make happy customers who return for more sales and leave good reviews. Conversely, a complex return process can result in negative feedback and customer loss.
4. Product Quality Enhancement
Returns management aids in identifying and rectifying product quality issues. By analysing return reasons, companies can uncover manufacturing or design defects. This ultimately enhances product quality and reduces future returns.
5. Legal Compliance
Complying with legal regulations in return policies is crucial. This includes consumer protection laws governing the handling and disposal of returned products. Adhering to these regulations helps businesses avoid costly fines and legal complications.
6. Competitive Edge
Well-designed returns policies can set a business apart from competitors. 84% of shoppers consider a retailer's return policy before making a purchase. A more lenient policy attracts a larger customer base compared to stricter policies.
7. Data-Driven Insights
Returns management generates valuable data for improving overall business performance. Tracking return reasons provides insights into customer preferences and product performance. This data informs data-driven decisions, leading to enhanced sales and marketing strategies.

What Is the True Cost of Retail Returns?
Returns in retail are unavoidable, but what retailers must recognize is the importance of the costs associated with return management. There are six hidden expenses that retail returns generate. Understanding them can help retailers strike a balance and support their retail business.
1. Shipping Costs
When a product is returned, it has to be picked up and taken back to the warehouse. If it's nearby, it's cheaper. But if it has to travel far, the cost goes up. For faulty product returns, there's more cost to send them to be fixed or recycled. Good logistics services help save some money here.
2. Customer Service Expenses
Handling retail returns involves customer service tasks like:
-
Assisting customers with return processing.
-
Coordinating with the logistics team.
-
Keeping customers informed about the return status until they receive their refund.
Sometimes, customer service might not always have real-time updates, leading to more customer interactions. Plus, eCommerce retailers provide customer support through various channels like phone, chat, email, and social media. It requires dedicated staff, which adds to the expense. As returns and customer service interactions increase, so do costs.
3. Operating Expenses
Handling returned items involves multiple steps, from inspecting and warehousing them to repairs, resale, and customer refunds. Each step adds to operational costs for retailers.
4. Cost of Depreciated Items
A high-quality product returned within the same season can be back on the shelf for online sale. However, as time goes by, the need to mark down the price can reduce demand, causing a decline in its perceived value.
Each returned item loses value due to processing time and costs. For instance, it's estimated that a $50 product return can cost around $33 to handle. Unfortunately, some retailers choose the easier and more cost-effective disposal of damaged returned goods, which ultimately find their way to landfills across the globe.
5. Environmental Costs
That brings us to the environmental consequence when returned items are discarded. In the US alone, returns create 5 billion pounds of waste annually. Also, in 2022, the return process, including shipping and packaging, caused around 24 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions, further harming the environment.
6. Reputation Costs
Retail returns harm a company's reputation. High return rates, negative reviews or customer complaints about the return process can tarnish a business's image, signalling potential issues with product quality or customer service. This can result in customer loss and reduced revenue.

Returns management Vs. Reverse Logistics
Returns management and reverse logistics are often used interchangeably, but they encompass different aspects of handling product returns.
Returns management primarily focuses on the customer-facing side of the retail return process. It includes return authorization, refunds, and customer satisfaction. It aims to make the return experience as painless as possible for customers.
On the other hand, reverse logistics is a broader concept that encompasses the entire journey of returned items. It involves the physical movement of products from the customer back to the retailer or manufacturer, decisions on whether to restock, refurbish, recycle, or dispose of the items, and the associated logistics management and supply chain processes.
In summary, returns management deals with customer experience and satisfaction, while reverse logistics covers the logistical and operational aspects of handling product returns. Both are essential components of efficient returns in retail.
Controllable and Uncontrollable Returns in Retail
Based on the reason behind the product return, retail returns often fall into two broad categories: controllable and uncontrollable. Understanding the difference between these two types is essential for effective returns management.
Controllable Returns
These are returns that retailers have some level of control over. They typically result from factors such as —
-
Lack of detailed product descriptions or high-quality images
-
Errors during picking and packing
-
Poor inventory management
-
Inaccuracies in retail fulfilment and shipments
-
Damage during transit due to subpar packaging
-
Misdelivery to the wrong address, and so on.
Retailers can actively work on reducing returns of controllable types and improving the overall customer experience through—
-
Collaboration with reputable suppliers for high-quality products.
-
Clear and accurate size charts for clothing.
-
Improved packaging to prevent shipping damages.
-
Careful and precise order fulfilment processes.
-
Partnering with reliable carriers.
-
Transparent order tracking to keep customers informed about delivery dates.
Uncontrollable Returns
These returns are beyond the retailer's direct control. They arise from factors like customer preferences, sizing issues, or simply changing one's mind about a purchase. While retailers can influence return rates through clear product descriptions, sizing guides, and exemplary customer service, they cannot entirely eliminate uncontrollable returns.
The takeaway here is that while you can't entirely prevent uncontrollable returns, you can be prepared for their seasonal surges and incorporate strategies to minimise their impact on your operations. The focus here is on making the return process as smooth as possible to retain customer loyalty.
Top 8 Ways to Create Seamless and Profitable Retail Returns Experiences
1. Reduce Product Returns from the Start
While seeking to make retail returns profitable, focus on reducing product returns at the outset. By minimising product returns from the very beginning, retailers can save both time and resources while enhancing customer satisfaction.
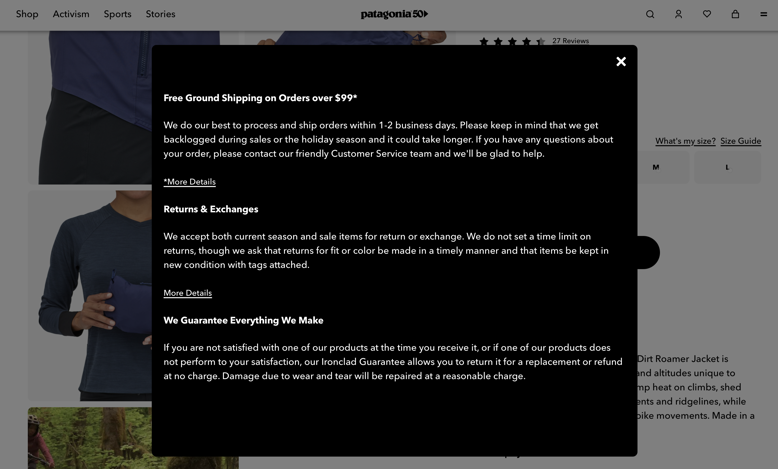
Patagonia—a leading brand in outdoor clothing and gear, is a great example of this. They offer a detailed fit guide and clear product information to eliminate any buyer confusion. Plus, their return and exchange process is hassle-free with minimal restrictions, making it easy for customers to initiate returns.
Here’s how:
-
Informative Product Details: Provide clear product information with high-quality images, descriptions, sizing guides, and specifications.
-
Customer Reviews: Encourage customer reviews to help buyers make informed decisions based on authentic feedback.
-
Size Charts and Fit Guides: Offer accurate size charts and fit guides for apparel and footwear.
-
User-Generated Content: Showcase real-life customer photos and videos for an authentic product experience.
-
Personalised Recommendations: Use data to suggest products aligned with customer preferences.
-
Virtual Try-Ons: Implement virtual try-on experiences for fashion items to reduce uncertainty.
-
Quality Control: Ensure products are in perfect condition before shipping to minimise defective product returns.
-
Clear Return Policies: Maintain a transparent return policy to deter impulsive product returns.
-
Educational Content: Provide product care and usage guidance to reduce improper handling.
-
Proactive Customer Support: Offer real-time assistance through chatbots or live chat for confident buying decisions.
2. Have a No-frills Retail Return Policy
By having a clear and simple retail return policy, you not only build trust with your customers but also reduce potential conflicts. Here's how to make it happen:
- Transparency: Ensure your return policy is easily accessible on your website and within the purchase process. Customers should be able to find it effortlessly.
- Clarity in Language: Use plain and simple language to make your policy easily understood by anyone. Avoid jargon or overly legal terms that might confuse customers.
- Return Timeframes: Clearly specify the timeframes within which returns are accepted. Whether it's 14 days, 30 days, or more, make sure it's explicitly mentioned.
- Eligibility Criteria: Define the conditions under which a product return can be accepted. This might include the product's condition, packaging, and whether certain items are exempt from returns.
![]()
- Return Methods: Explain how customers can initiate a return. Whether it's through your website, email, or a dedicated return portal, provide step-by-step guidance.
- Refund Options: Be explicit about the refund options available—store credit, full refund, or exchange. This helps customers make informed choices.
- Return Shipping: Clarify who covers return shipping costs. Will it be the customer, your company, or a shared responsibility?
- Communication Channels: Clearly state how customers can reach out for support or inquiries regarding returns. Make sure they know where to go for assistance.
- Exception Handling: Anticipate exceptional situations, such as defective product returns or shipping errors. Outline how these will be handled to reassure customers.
- Regular Updates: Review and update your return policy as necessary. Changes in regulations or customer feedback may require adjustments to keep it relevant.

3. Implement a User-Friendly Returns Portal
Another essential tool for frictionless retail return management is a user-friendly returns portal. This digital gateway streamlines the returns process, making it efficient and hassle-free.
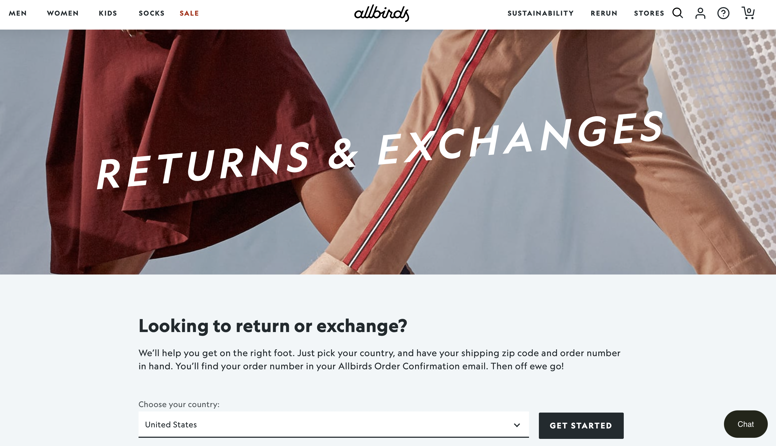
That’s the most important takeaway from Allbirds—a sustainable footwear brand. Its hassle-free return portal and concise return policy leave no lift on the customer's end. Take a look:
Here's how to do it right:
-
Centralised Returns Hub: Help customers initiate returns, track progress, and communicate with your support team in one convenient location.
-
Easy Navigation: Design your portal with user-friendliness in mind. Intuitive navigation, clear instructions, and a visually appealing interface enhance the user experience.
-
Accessible Across Devices: Ensure your portal is accessible across various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and desktops. Customers appreciate the flexibility to process returns from their preferred device.
-
Step-by-Step Guidance: Reduce confusion by offering step-by-step guidance throughout the retail return process.
-
Instant Return Authorization: Implement an automated return authorization process, allowing customers to receive return approval swiftly. The quicker the authorization, the sooner the return process begins.
-
Real-Time Tracking: Enable real-time tracking of return shipments. Customers should know the status of their return from the moment it's initiated to its final resolution.
-
Communication Channel: Integrate a direct communication channel within the portal for customers to seek assistance or clarify doubts promptly.
-
Feedback Collection: Use the portal to collect feedback on the return experience and use the insights to guide improvements.
-
Information Repository: Include comprehensive information on your return policy, eligibility criteria, and FAQs within the portal. Customers should find answers to common queries without the need for external resources.
-
Security Measures: Prioritise security to protect customer data. Implement encryption and secure authentication methods to instil confidence in the portal's safety.
4. Automate Your Return Management Workflow
Automation in your returns management workflow brings efficiency, cost savings, and precision into the retail return process. You can also use dedicated returns software for retailers to give your customers the ability to choose their options on their own. Here's how to make automation work for your retail returns:
- Returns Initiation: Implement an automated system that allows customers to initiate returns easily. Whether through your website or a dedicated portal, make the process straightforward and user-friendly.
- Return Authorization: Automate the return authorization process. Algorithms can quickly determine if a return request meets your policy criteria, expediting approvals for eligible returns.
- Label Generation: Use automated systems to generate return labels and shipping documents. This reduces manual data entry errors and ensures accurate shipping information.
- Inventory Updates: Integrate your return system with inventory management. When a returned item is authorised, your inventory should automatically reflect its availability for restocking or refurbishment.
- Communication: Automate email notifications to keep customers informed at every step. Send confirmation emails upon return initiation, approval, receipt of the returned item, and resolution.
- Data Analysis: Leverage automation to gather and analyse return data. Identify trends, such as common reasons for returns, and use this information to make data-driven decisions.
- Refund Processing: Use automated financial systems to process refunds swiftly and accurately. Ensure customers receive their refunds without unnecessary delays.
5. Collect and Analyse Product Returns Data
To avoid the hassle of product returns, you must take time to understand why customers return products. Collecting and analysing product returns data helps you do that. Here's how to make the most of this data to reduce returns in retail:
-
Comprehensive Data: Gather detailed data on every return, including reasons for return, product condition, and return location. The more information you have, the better you can identify patterns.
-
Identify Trends: Look for recurring issues or trends in the data. Are certain products frequently returned due to specific defects? Is there a common reason for returns during a particular season?
-
Root Cause Analysis: Dive deep into the data to uncover the root causes of returns. Are there consistent issues in your supply chain, like mishandling during shipping or poor packaging?
-
Customer Feedback: Incorporate customer feedback, reviews, and surveys into your data analysis to understand their experiences and pain points.
-
Product Improvement: Use feedback from retail returns data to drive product improvements.
-
Supplier Collaboration: Share returns data with suppliers to address recurring quality issues. This collaboration can lead to better product quality.
-
Returns Prediction: With historical data, you can develop predictive models to anticipate returns, helping you allocate resources more effectively.
-
Cost Reduction: Identify areas where returns are costing you the most and find ways to reduce these costs. This might involve optimising packaging or streamlining logistics.
6. Optimise Inventory Management and Stock Replenishment
Effectively managing your inventory plays a pivotal role in handling returns efficiently, especially in the face of changing customer behaviours. Here's a fresh perspective on optimising your inventory:
-
Dynamic Inventory Visibility: Ensure that returned items deemed resellable are promptly marked as "in stock" on your website or in-store.
-
Strategic Storage: Invest in strategic storage solutions that maximise your storage capacity. Consider vertical storage systems or efficient shelving layouts to make the most of your available space.
-
Real-Time Inventory Software: Consider adopting advanced inventory management software capable of real-time tracking and updates. Such software provides instant visibility into your stock levels and helps prevent overstocking or stockouts.
-
Returns Segmentation: Categorize returned items into segments based on their condition and potential for resale. This segmentation allows you to prioritise restocking efforts for high-value, like-new products.
-
Efficient Returns Handling: Streamline the returns handling process to minimise storage time. Implement efficient workflows that quickly assess returned items, make refurbishment decisions, and return them to the sales floor.
-
Inventory Audits: Conduct regular inventory audits to identify discrepancies and inconsistencies. These audits help maintain data accuracy and minimise the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
-
Supplier Relationship Management: Maintain open communication with your suppliers to ensure timely restocking of popular items. Collaborative supplier relationships can help you respond swiftly to changing demands.
7. Streamline Return Transportation and Logistics
While reducing returns is a priority, it's equally vital to establish robust processes for efficiently handling returned products when they re-enter the supply chain. Hence, implementing streamlined transportation and reverse logistics procedures for managing returned items is essential.
-
Carrier Collaboration: Foster strong partnerships with reputable carriers and logistics providers. Collaborate with carriers known for their efficiency and timely deliveries, especially concerning return shipments.
-
Prepaid Return Labels: Provide customers with prepaid return labels, simplifying the return shipping operations.
-
Return Package Tracking: Implement robust tracking systems that enable customers to monitor the status of their return packages in real time.
-
Centralised Return Centers: Centralize return processing in dedicated return centres. They expedite the inspection, refurbishment, and restocking processes, resulting in quicker turnaround times.
-
Customer-Friendly Return Scheduling: Empower customers to schedule return pickups or drop-offs at their convenience. Flexible scheduling options reduce disruptions associated with returns.
8. Outsource Your Ecommerce Retail Returns to a 3PL
While improving returns management can be a substantial task, many ecommerce brands opt to collaborate with a third-party logistics (3PL) partner like PACK & SEND to turbocharge their retail returns reverse logistics.
Here’s how working with PACK & SEND can help you manage the reverse logistics of your retail returns:
-
Expertise in Returns Management: We bring in-depth expertise and experience to handle eCommerce retail returns efficiently.
-
Scalability: With a 3PL service, you gain the flexibility to scale your returns management operations according to your business's needs. Whether it's peak holiday season or routine procedures, we adapt to fluctuations in returns volume.
-
Streamlined Processes: Our well-established returns processes and infrastructure, translate into faster and consistent handling of returned items.
-
Geographic Coverage: Our extensive network of shipping partners enables you to optimise return transportation and reduce shipping costs.
-
Technology Integration:We offer real-time visibility into return inventory, tracking, and reporting. This technology empowers you with valuable data insights to enhance your returns strategy.
-
Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing can help control costs by reducing the need for in-house resources dedicated to returns processing. Additionally, you benefit from our economies of scale in logistics operations.
-
Focus on Core Competencies: Delegating returns management to a 3PL frees your team to concentrate on core business activities.
-
Compliance and Regulation: As a well-established 3PL, we are well-versed in regulatory requirements and compliance standards related to returns.

Conclusion
Retailers should view product returns as opportunities rather than obstacles, as they are an integral part of retail operations. While preventing retail returns may be challenging, they don't have to be a burden on your business. You can streamline returns management for greater efficiency and profitability.
By establishing a clear return policy, taking preventive measures, following detailed return handling procedures, and implementing a robust reverse logistics system, you can substantially lessen the impact of product returns on your overall profitability.
Ready to take the hassle out of managing your retail returns and optimise your eCommerce order fulfilment? Our PACK & SEND experts are here to help you succeed. Get in touch with us today to unlock the solutions your business deserves
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a retail return?
A retail return refers to the process of a customer bringing back a purchased product to the retailer for various reasons. This can include issues like product defects, dissatisfaction with the item, wrong size or colour, or a change of mind. The retailer then typically assesses the condition of the returned item. And they may offer a refund, exchange, store credit, or repair, depending on their return policy.
How long do retail returns take to process?
Return processing times vary based on the retailer's policy and the nature of the return. In some cases, returns are processed relatively quickly. In that case, customers may receive their refund or exchange within a few days.
During busy return seasons, return processing may take longer due to the high volume of returns. Retailers often specify their return processing times in their return policies.
What do retail stores do with returns?
Retail stores handle returns in various ways based on the condition of the returned item. If the product is in new, resalable condition, it may be restocked and put back on the shelves for resale. If the item is damaged, it might be sent for refurbishment, repair, or recycling. In some cases, returned items are returned to the original vendors or suppliers.
Does the retailer issue a refund for returns?
Retailers often issue refunds as one of the options for customers returning products. But it depends on the retailer's return policy and the customer's preference. Some retailers offer refunds to the original payment. In contrast, others may offer store credit, exchanges, or product repairs.
Here's a quick riddle for you: What's a challenge that both retailers and customers face but see differently? If you guessed "retail returns," you're right on the mark!
For customers, retail returns are like a safety net. Returns ensure they're satisfied with their purchases. They are customers’ way of making sure they always get what they want.
But for retailers, eCommerce retail returns can be a bit more complicated. It involves handling the reverse logistics and item restocking and managing its financial impact. Mishandled, they can eat into profits and create operational headaches.
In this blog, we'll dive into retail returns and why they matter for retailers. We'll discuss ways to improve product returns management and turn them into assets.
What is a Retail Return?
A retail return is a process initiated by a customer wishing to return a purchased product. This could be due to various reasons. Such as not liking the product, receiving a damaged item, or changing their mind. The retailer's role is to handle product returns, offering a refund or a replacement.

Let's say you operate an online clothing store. A customer who recently bought a dress. A customer contacts your customer support to start a return because of the size issues. As the retailer, your job is to guide the customer on how to return the dress. This might include giving them retail return instructions and a return label. Once you receive the dress in good condition, you can either refund or offer a replacement.
How Does the "Product Returns" Process Work?
The returns process, also known as reverse logistics, unfolds in several steps:
Step 1: Retail Returns Initiation
The process begins when a customer decides to return a product, from an online or offline store. The customer specifies reasons for returns. They also state whether they want an exchange or refund.
Step 2: Approval or Disapproval
On assessing the request, the company decides whether to proceed with the return. Some companies engage third-party logistics (3PL) providers to streamline return and retail fulfilment.
Step 3: Receiving Returned Products
The 3PL collects the product return from the customer and delivers it to a designated location. The retailer then conducts a physical inspection of the returned product as per its return policy. They must choose whether to recycle the item for useful parts, repair or refurbish it, resell it, or dispose of it.
Step 4: Refund Process
Based on the product's condition and return policy, retailers figure out its response. It might involve offering a refund, exchange, store credit, or product repair.

What Is Retail Returns Management and Why Is It Important?
Returns management is the systematic process by which retailers and eCommerce stores handle and control product returns initiated by customers. It combines elements of customer support, logistics, and inventory management.
Returns Management focuses on the efficient handling of returns in retail. This is crucial for businesses because it directly impacts customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and overall profitability of the business.
Efficiently handling product returns can lead to substantial cost savings by repurposing undamaged items and restocking them for future resale.
Product returns in eCommerce often present greater complexity compared to brick-and-mortar stores. That’s because eCommerce returns often involve returning the product back to the seller, adding more costs and logistical challenges to the mix.
Here are the key steps in a return management process:
1. Return Request: Customer requests a return due to defective or incorrect items or dissatisfaction.
2. Review for Authorization: Retailer checks return requests against their return policy (timeframe, eligibility).
3. Generate Return Label: Approved returns receive a shipping label for customer use.
4. Secure Packaging: The customer ensures the item is packaged with all accessories, tags, and packaging.
5. Ship the Return: The customer sends the item using the provided label or designated method.
6. Receive and Inspect: Retailer receives, inspects for damage, and checks completeness.
7. Disposition Decision: The retailer decides on restocking, refurbishing, recycling, or disposal.
8. Resolution: The retailer discusses resolution options with the customer (refund, exchange, credit, or repair).
9. Process Refund/Exchange: The retailer implements the chosen resolution.
10. Update Inventory: Retailer adjusts inventory based on disposition decision.
11. Data Analysis: Analyze return data for trends, product return issues, and process improvements.
12. Reverse Logistics: Reverse logistics for returns to the manufacturer or supplier. May involve transportation coordination and inventory management.

Why Is Retail Returns Management Important?
Retail returns, especially in online shopping, have evolved into a well-established practice. When we buy stuff online, we can't try it out first. So, having the option to return items for free is something most stores offer.
So much so that the concept of free returns is being carried over across all retail channels thanks to omnichannel retail. In the past, you could only return things if the store didn't meet your expectations. But now, it's much easier to return things for any reason, even if you just changed your mind.
However, the traditional retail supply chain is linear, typically ending when the product reaches the consumer. Any product reentering the supply chain after the sale is seen as an 'exception.' Handling these exceptions is both expensive and complicated. It increases the cost of service and reduces profit margins.
In recent years, rising product returns have worried retailers and their profits.
According to a study by SML, in 2022, retailers found that about 30% of their sales resulted in returns. This is significantly higher than the 10% returns level of in-store purchases.
Furthermore, on average, about 42% of these returns were resold at a lower price, and 12% were not resold. Retailers mentioned that the average discount applied to these items was around 38%.
High return rates are clearly taking a significant bite out of retailer profits. In the current economic climate, businesses can't ignore this challenge any longer. Retailers should view retail returns as an integral part of the customer journey. Handling returns right can boost customer loyalty and advocacy.
To address this issue effectively, retailers need a streamlined and cost-effective return management process that ensures returned items can be quickly reintroduced for sale.
Here are some more reasons to have efficient retail returns management:
1. Cost Savings
Effective returns management can help with significant cost savings. Restocking fees or store credit instead of refunds can help control expenses. Moreover, streamlining the return process reduces costs linked to shipping and handling.
2. Inventory Optimization
Returns management contributes to better inventory control. It ensures efficient flow of returned products through the supply chain. It also addresses the financial impacts of lost sales and restocking. Tracking product returns helps adjust stocking strategies, reducing excess inventory and enhancing efficiency.
3. Customer Delight
Smooth returns make happy customers who return for more sales and leave good reviews. Conversely, a complex return process can result in negative feedback and customer loss.
4. Product Quality Enhancement
Returns management aids in identifying and rectifying product quality issues. By analysing return reasons, companies can uncover manufacturing or design defects. This ultimately enhances product quality and reduces future returns.
5. Legal Compliance
Complying with legal regulations in return policies is crucial. This includes consumer protection laws governing the handling and disposal of returned products. Adhering to these regulations helps businesses avoid costly fines and legal complications.
6. Competitive Edge
Well-designed returns policies can set a business apart from competitors. 84% of shoppers consider a retailer's return policy before making a purchase. A more lenient policy attracts a larger customer base compared to stricter policies.
7. Data-Driven Insights
Returns management generates valuable data for improving overall business performance. Tracking return reasons provides insights into customer preferences and product performance. This data informs data-driven decisions, leading to enhanced sales and marketing strategies.

What Is the True Cost of Retail Returns?
Returns in retail are unavoidable, but what retailers must recognize is the importance of the costs associated with return management. There are six hidden expenses that retail returns generate. Understanding them can help retailers strike a balance and support their retail business.
1. Shipping Costs
When a product is returned, it has to be picked up and taken back to the warehouse. If it's nearby, it's cheaper. But if it has to travel far, the cost goes up. For faulty product returns, there's more cost to send them to be fixed or recycled. Good logistics services help save some money here.
2. Customer Service Expenses
Handling retail returns involves customer service tasks like:
-
Assisting customers with return processing.
-
Coordinating with the logistics team.
-
Keeping customers informed about the return status until they receive their refund.
Sometimes, customer service might not always have real-time updates, leading to more customer interactions. Plus, eCommerce retailers provide customer support through various channels like phone, chat, email, and social media. It requires dedicated staff, which adds to the expense. As returns and customer service interactions increase, so do costs.
3. Operating Expenses
Handling returned items involves multiple steps, from inspecting and warehousing them to repairs, resale, and customer refunds. Each step adds to operational costs for retailers.
4. Cost of Depreciated Items
A high-quality product returned within the same season can be back on the shelf for online sale. However, as time goes by, the need to mark down the price can reduce demand, causing a decline in its perceived value.
Each returned item loses value due to processing time and costs. For instance, it's estimated that a $50 product return can cost around $33 to handle. Unfortunately, some retailers choose the easier and more cost-effective disposal of damaged returned goods, which ultimately find their way to landfills across the globe.
5. Environmental Costs
That brings us to the environmental consequence when returned items are discarded. In the US alone, returns create 5 billion pounds of waste annually. Also, in 2022, the return process, including shipping and packaging, caused around 24 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions, further harming the environment.
6. Reputation Costs
Retail returns harm a company's reputation. High return rates, negative reviews or customer complaints about the return process can tarnish a business's image, signalling potential issues with product quality or customer service. This can result in customer loss and reduced revenue.

Returns management Vs. Reverse Logistics
Returns management and reverse logistics are often used interchangeably, but they encompass different aspects of handling product returns.
Returns management primarily focuses on the customer-facing side of the retail return process. It includes return authorization, refunds, and customer satisfaction. It aims to make the return experience as painless as possible for customers.
On the other hand, reverse logistics is a broader concept that encompasses the entire journey of returned items. It involves the physical movement of products from the customer back to the retailer or manufacturer, decisions on whether to restock, refurbish, recycle, or dispose of the items, and the associated logistics management and supply chain processes.
In summary, returns management deals with customer experience and satisfaction, while reverse logistics covers the logistical and operational aspects of handling product returns. Both are essential components of efficient returns in retail.
Controllable and Uncontrollable Returns in Retail
Based on the reason behind the product return, retail returns often fall into two broad categories: controllable and uncontrollable. Understanding the difference between these two types is essential for effective returns management.
Controllable Returns
These are returns that retailers have some level of control over. They typically result from factors such as —
-
Lack of detailed product descriptions or high-quality images
-
Errors during picking and packing
-
Poor inventory management
-
Inaccuracies in retail fulfilment and shipments
-
Damage during transit due to subpar packaging
-
Misdelivery to the wrong address, and so on.
Retailers can actively work on reducing returns of controllable types and improving the overall customer experience through—
-
Collaboration with reputable suppliers for high-quality products.
-
Clear and accurate size charts for clothing.
-
Improved packaging to prevent shipping damages.
-
Careful and precise order fulfilment processes.
-
Partnering with reliable carriers.
-
Transparent order tracking to keep customers informed about delivery dates.
Uncontrollable Returns
These returns are beyond the retailer's direct control. They arise from factors like customer preferences, sizing issues, or simply changing one's mind about a purchase. While retailers can influence return rates through clear product descriptions, sizing guides, and exemplary customer service, they cannot entirely eliminate uncontrollable returns.
The takeaway here is that while you can't entirely prevent uncontrollable returns, you can be prepared for their seasonal surges and incorporate strategies to minimise their impact on your operations. The focus here is on making the return process as smooth as possible to retain customer loyalty.
Top 8 Ways to Create Seamless and Profitable Retail Returns Experiences
1. Reduce Product Returns from the Start
While seeking to make retail returns profitable, focus on reducing product returns at the outset. By minimising product returns from the very beginning, retailers can save both time and resources while enhancing customer satisfaction.
Patagonia—a leading brand in outdoor clothing and gear, is a great example of this. They offer a detailed fit guide and clear product information to eliminate any buyer confusion. Plus, their return and exchange process is hassle-free with minimal restrictions, making it easy for customers to initiate returns.

Here’s how:
-
Informative Product Details: Provide clear product information with high-quality images, descriptions, sizing guides, and specifications.
-
Customer Reviews: Encourage customer reviews to help buyers make informed decisions based on authentic feedback.
-
Size Charts and Fit Guides: Offer accurate size charts and fit guides for apparel and footwear.
-
User-Generated Content: Showcase real-life customer photos and videos for an authentic product experience.
-
Personalised Recommendations: Use data to suggest products aligned with customer preferences.
-
Virtual Try-Ons: Implement virtual try-on experiences for fashion items to reduce uncertainty.
-
Quality Control: Ensure products are in perfect condition before shipping to minimise defective product returns.
-
Clear Return Policies: Maintain a transparent return policy to deter impulsive product returns.
-
Educational Content: Provide product care and usage guidance to reduce improper handling.
-
Proactive Customer Support: Offer real-time assistance through chatbots or live chat for confident buying decisions.
2. Have a No-frills Retail Return Policy
By having a clear and simple retail return policy, you not only build trust with your customers but also reduce potential conflicts. Here's how to make it happen:
- Transparency: Ensure your return policy is easily accessible on your website and within the purchase process. Customers should be able to find it effortlessly.
- Clarity in Language: Use plain and simple language to make your policy easily understood by anyone. Avoid jargon or overly legal terms that might confuse customers.
- Return Timeframes: Clearly specify the timeframes within which returns are accepted. Whether it's 14 days, 30 days, or more, make sure it's explicitly mentioned.
- Eligibility Criteria: Define the conditions under which a product return can be accepted. This might include the product's condition, packaging, and whether certain items are exempt from returns.
![]()
- Return Methods: Explain how customers can initiate a return. Whether it's through your website, email, or a dedicated return portal, provide step-by-step guidance.
- Refund Options: Be explicit about the refund options available—store credit, full refund, or exchange. This helps customers make informed choices.
- Return Shipping: Clarify who covers return shipping costs. Will it be the customer, your company, or a shared responsibility?
- Communication Channels: Clearly state how customers can reach out for support or inquiries regarding returns. Make sure they know where to go for assistance.
- Exception Handling: Anticipate exceptional situations, such as defective product returns or shipping errors. Outline how these will be handled to reassure customers.
- Regular Updates: Review and update your return policy as necessary. Changes in regulations or customer feedback may require adjustments to keep it relevant.

3. Implement a User-Friendly Returns Portal
Another essential tool for frictionless retail return management is a user-friendly returns portal. This digital gateway streamlines the returns process, making it efficient and hassle-free.
That’s the most important takeaway from Allbirds—a sustainable footwear brand. Its hassle-free return portal and concise return policy leave no lift on the customer's end. Take a look:

Here's how to do it right:
-
Centralised Returns Hub: Help customers initiate returns, track progress, and communicate with your support team in one convenient location.
-
Easy Navigation: Design your portal with user-friendliness in mind. Intuitive navigation, clear instructions, and a visually appealing interface enhance the user experience.
-
Accessible Across Devices: Ensure your portal is accessible across various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and desktops. Customers appreciate the flexibility to process returns from their preferred device.
-
Step-by-Step Guidance: Reduce confusion by offering step-by-step guidance throughout the retail return process.
-
Instant Return Authorization: Implement an automated return authorization process, allowing customers to receive return approval swiftly. The quicker the authorization, the sooner the return process begins.
-
Real-Time Tracking: Enable real-time tracking of return shipments. Customers should know the status of their return from the moment it's initiated to its final resolution.
-
Communication Channel: Integrate a direct communication channel within the portal for customers to seek assistance or clarify doubts promptly.
-
Feedback Collection: Use the portal to collect feedback on the return experience and use the insights to guide improvements.
-
Information Repository: Include comprehensive information on your return policy, eligibility criteria, and FAQs within the portal. Customers should find answers to common queries without the need for external resources.
-
Security Measures: Prioritise security to protect customer data. Implement encryption and secure authentication methods to instil confidence in the portal's safety.
4. Automate Your Return Management Workflow
Automation in your returns management workflow brings efficiency, cost savings, and precision into the retail return process. You can also use dedicated returns software for retailers to give your customers the ability to choose their options on their own. Here's how to make automation work for your retail returns:
- Returns Initiation: Implement an automated system that allows customers to initiate returns easily. Whether through your website or a dedicated portal, make the process straightforward and user-friendly.
- Return Authorization: Automate the return authorization process. Algorithms can quickly determine if a return request meets your policy criteria, expediting approvals for eligible returns.
- Label Generation: Use automated systems to generate return labels and shipping documents. This reduces manual data entry errors and ensures accurate shipping information.
- Inventory Updates: Integrate your return system with inventory management. When a returned item is authorised, your inventory should automatically reflect its availability for restocking or refurbishment.
- Communication: Automate email notifications to keep customers informed at every step. Send confirmation emails upon return initiation, approval, receipt of the returned item, and resolution.
- Data Analysis: Leverage automation to gather and analyse return data. Identify trends, such as common reasons for returns, and use this information to make data-driven decisions.
- Refund Processing: Use automated financial systems to process refunds swiftly and accurately. Ensure customers receive their refunds without unnecessary delays.
5. Collect and Analyse Product Returns Data
To avoid the hassle of product returns, you must take time to understand why customers return products. Collecting and analysing product returns data helps you do that. Here's how to make the most of this data to reduce returns in retail:
-
Comprehensive Data: Gather detailed data on every return, including reasons for return, product condition, and return location. The more information you have, the better you can identify patterns.
-
Identify Trends: Look for recurring issues or trends in the data. Are certain products frequently returned due to specific defects? Is there a common reason for returns during a particular season?
-
Root Cause Analysis: Dive deep into the data to uncover the root causes of returns. Are there consistent issues in your supply chain, like mishandling during shipping or poor packaging?
-
Customer Feedback: Incorporate customer feedback, reviews, and surveys into your data analysis to understand their experiences and pain points.
-
Product Improvement: Use feedback from retail returns data to drive product improvements.
-
Supplier Collaboration: Share returns data with suppliers to address recurring quality issues. This collaboration can lead to better product quality.
-
Returns Prediction: With historical data, you can develop predictive models to anticipate returns, helping you allocate resources more effectively.
-
Cost Reduction: Identify areas where returns are costing you the most and find ways to reduce these costs. This might involve optimising packaging or streamlining logistics.
6. Optimise Inventory Management and Stock Replenishment
Effectively managing your inventory plays a pivotal role in handling returns efficiently, especially in the face of changing customer behaviours. Here's a fresh perspective on optimising your inventory:
-
Dynamic Inventory Visibility: Ensure that returned items deemed resellable are promptly marked as "in stock" on your website or in-store.
-
Strategic Storage: Invest in strategic storage solutions that maximise your storage capacity. Consider vertical storage systems or efficient shelving layouts to make the most of your available space.
-
Real-Time Inventory Software: Consider adopting advanced inventory management software capable of real-time tracking and updates. Such software provides instant visibility into your stock levels and helps prevent overstocking or stockouts.
-
Returns Segmentation: Categorize returned items into segments based on their condition and potential for resale. This segmentation allows you to prioritise restocking efforts for high-value, like-new products.
-
Efficient Returns Handling: Streamline the returns handling process to minimise storage time. Implement efficient workflows that quickly assess returned items, make refurbishment decisions, and return them to the sales floor.
-
Inventory Audits: Conduct regular inventory audits to identify discrepancies and inconsistencies. These audits help maintain data accuracy and minimise the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
-
Supplier Relationship Management: Maintain open communication with your suppliers to ensure timely restocking of popular items. Collaborative supplier relationships can help you respond swiftly to changing demands.
7. Streamline Return Transportation and Logistics
While reducing returns is a priority, it's equally vital to establish robust processes for efficiently handling returned products when they re-enter the supply chain. Hence, implementing streamlined transportation and reverse logistics procedures for managing returned items is essential.
-
Carrier Collaboration: Foster strong partnerships with reputable carriers and logistics providers. Collaborate with carriers known for their efficiency and timely deliveries, especially concerning return shipments.
-
Prepaid Return Labels: Provide customers with prepaid return labels, simplifying the return shipping operations.
-
Return Package Tracking: Implement robust tracking systems that enable customers to monitor the status of their return packages in real time.
-
Centralised Return Centers: Centralize return processing in dedicated return centres. They expedite the inspection, refurbishment, and restocking processes, resulting in quicker turnaround times.
-
Customer-Friendly Return Scheduling: Empower customers to schedule return pickups or drop-offs at their convenience. Flexible scheduling options reduce disruptions associated with returns.
8. Outsource Your Ecommerce Retail Returns to a 3PL
While improving returns management can be a substantial task, many ecommerce brands opt to collaborate with a third-party logistics (3PL) partner like PACK & SEND to turbocharge their retail returns reverse logistics.
Here’s how working with PACK & SEND can help you manage the reverse logistics of your retail returns:
-
Expertise in Returns Management: We bring in-depth expertise and experience to handle eCommerce retail returns efficiently.
-
Scalability: With a 3PL service, you gain the flexibility to scale your returns management operations according to your business's needs. Whether it's peak holiday season or routine procedures, we adapt to fluctuations in returns volume.
-
Streamlined Processes: Our well-established returns processes and infrastructure, translate into faster and consistent handling of returned items.
-
Geographic Coverage: Our extensive network of shipping partners enables you to optimise return transportation and reduce shipping costs.
-
Technology Integration: We offer real-time visibility into return inventory, tracking, and reporting. This technology empowers you with valuable data insights to enhance your returns strategy.
-
Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing can help control costs by reducing the need for in-house resources dedicated to returns processing. Additionally, you benefit from our economies of scale in logistics operations.
-
Focus on Core Competencies: Delegating returns management to a 3PL frees your team to concentrate on core business activities.
-
Compliance and Regulation: As a well-established 3PL, we are well-versed in regulatory requirements and compliance standards related to returns.

Conclusion
Retailers should view product returns as opportunities rather than obstacles, as they are an integral part of retail operations. While preventing retail returns may be challenging, they don't have to be a burden on your business. You can streamline returns management for greater efficiency and profitability.
By establishing a clear return policy, taking preventive measures, following detailed return handling procedures, and implementing a robust reverse logistics system, you can substantially lessen the impact of product returns on your overall profitability.
Ready to take the hassle out of managing your retail returns and optimise your eCommerce order fulfilment? Our PACK & SEND experts are here to help you succeed. Get in touch with us today to unlock the solutions your business deserves
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a retail return?
A retail return refers to the process of a customer bringing back a purchased product to the retailer for various reasons. This can include issues like product defects, dissatisfaction with the item, wrong size or colour, or a change of mind. The retailer then typically assesses the condition of the returned item. And they may offer a refund, exchange, store credit, or repair, depending on their return policy.
How long do retail returns take to process?
Return processing times vary based on the retailer's policy and the nature of the return. In some cases, returns are processed relatively quickly. In that case, customers may receive their refund or exchange within a few days.
During busy return seasons, return processing may take longer due to the high volume of returns. Retailers often specify their return processing times in their return policies.
What do retail stores do with returns?
Retail stores handle returns in various ways based on the condition of the returned item. If the product is in new, resalable condition, it may be restocked and put back on the shelves for resale. If the item is damaged, it might be sent for refurbishment, repair, or recycling. In some cases, returned items are returned to the original vendors or suppliers.
Does the retailer issue a refund for returns?
Retailers often issue refunds as one of the options for customers returning products. But it depends on the retailer's return policy and the customer's preference. Some retailers offer refunds to the original payment. In contrast, others may offer store credit, exchanges, or product repairs.
